Hip replacement surgery guide in 2024
Contents
1 # What is hip replacement?
2# Refined, processed and packaged foods:
3# How is hip replacement surgery done?
4# What types of materials are hip prostheses made of?
5# What is the surgical program and how is it performed?
6# What not to do after hip replacement surgery?
7# What are the pathologies and problems that may require a hip prosthesis?
8# What are the contraindications to a total or semi-total hip replacement?
9# What are the general guidelines about taking the decision of a hip replacement surgery?
10# What are the general guidelines about taking the decision of a hip replacement surgery?
11# Which exams have to be done before a hip replacement surgery?
12# What are the complications after hip replacement surgery?
13# How long does a hip replacement last?
This is the most comprehensive guide to hip replacement surgery.
In particular, we're going to clear up:
- what are the pros and cons about the surgery;
- what are the post-operative risks and possible complications;
- what are the do's and don'ts after the prosthesis surgery;
Let’s get started.
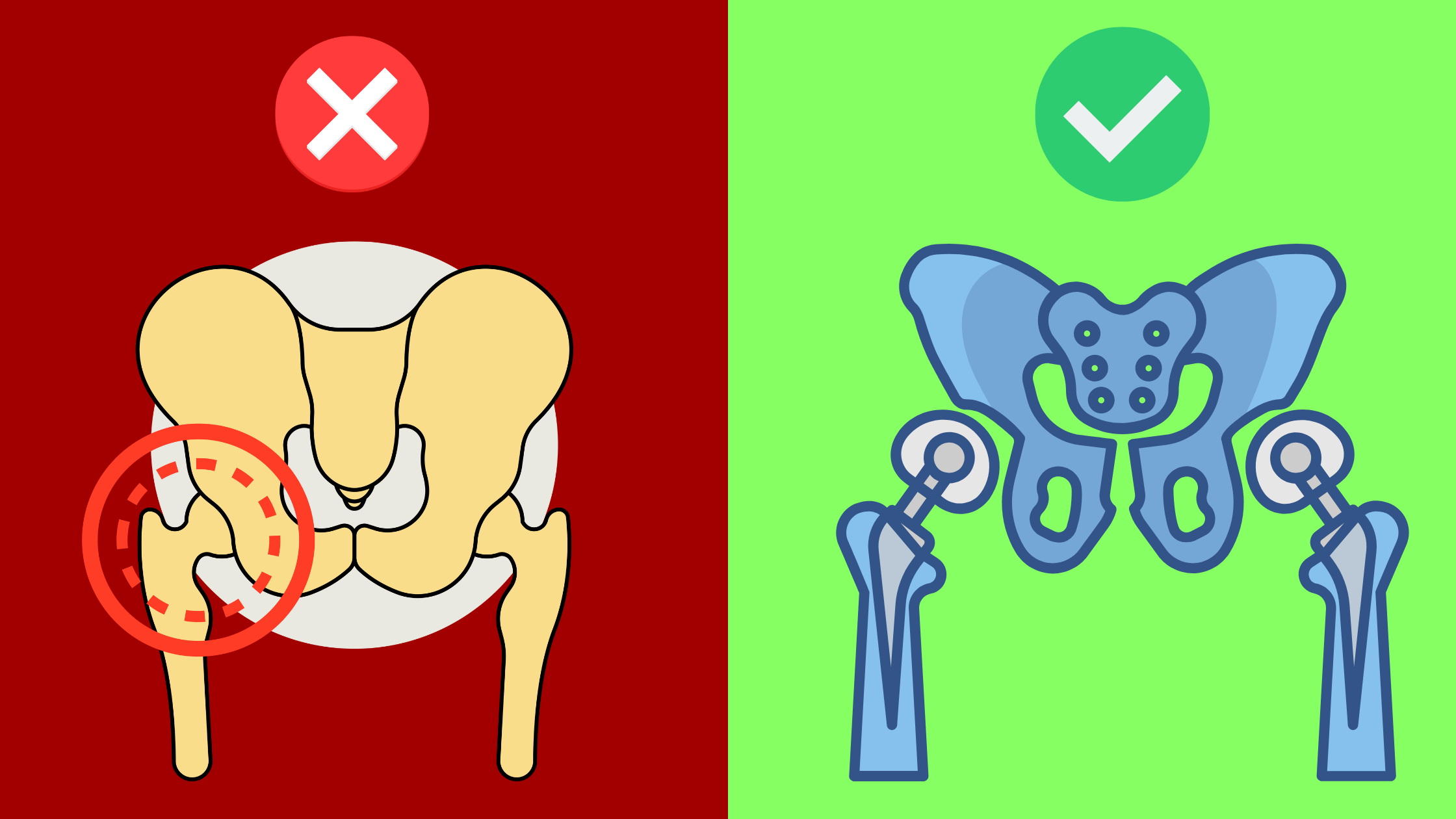
What is hip replacement?
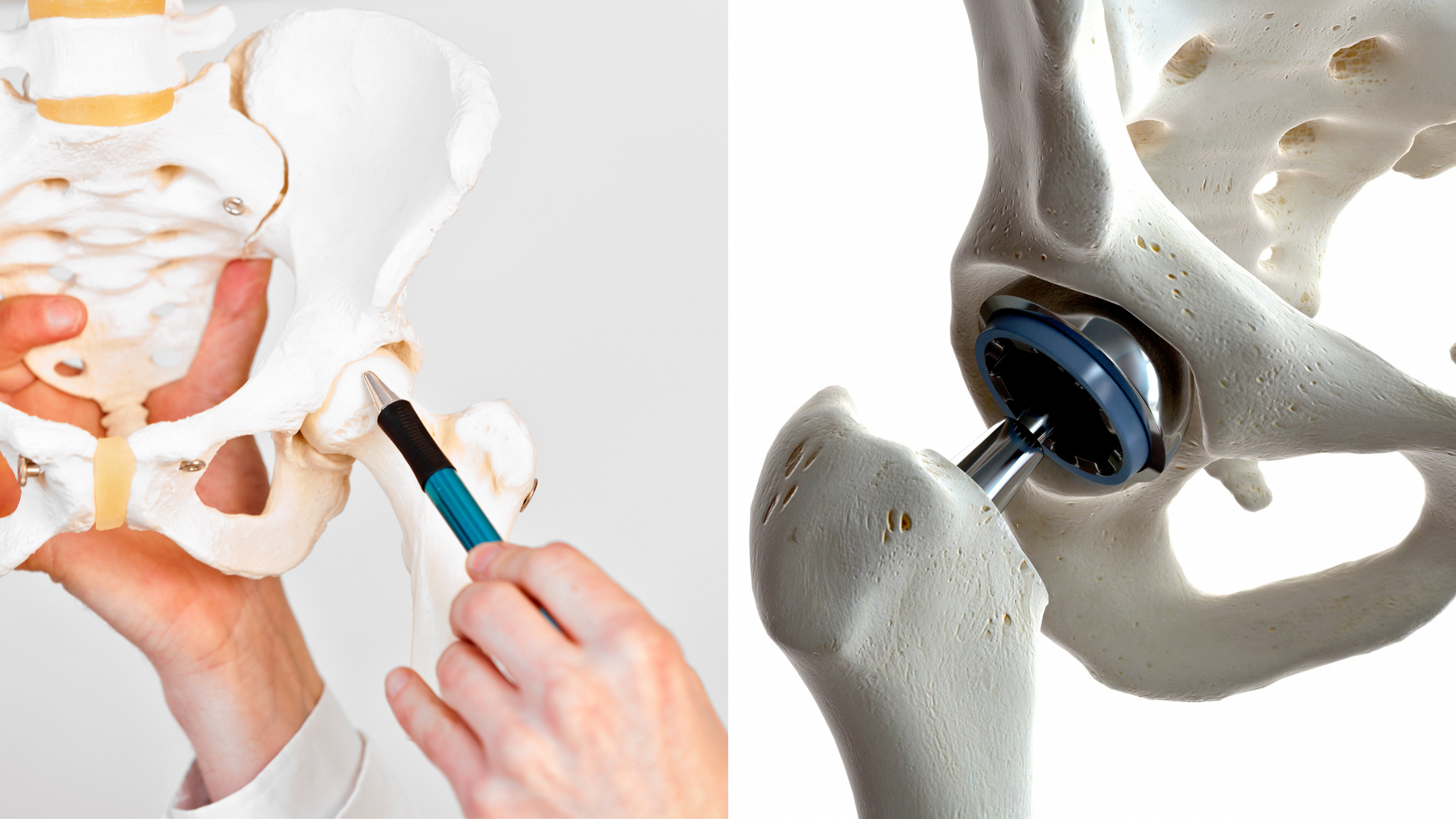
Hip replacement is the substitution of the hip joint with an artificial prosthesis.
It is the most complex surgical treatment to fix a compound fracture of the femoral neck.
The replacement can be:
- Total (also called arthroplasty): the head of the femur and the concave component of the hip, the cup, are completely replaced;
- Partial (endoprosthesis): it only consists in the substitution of the femoral portion;
- Resurfaced: the femoral head is not removed but completely resurfaced, capped with a smooth metal covering;
- Cemented: in very elderly patients, with poor bone quality and/or in the presence of associated bone pathologies (such as osteoporosis), an acrylic cement is applied to give more stability to the prosthesis.
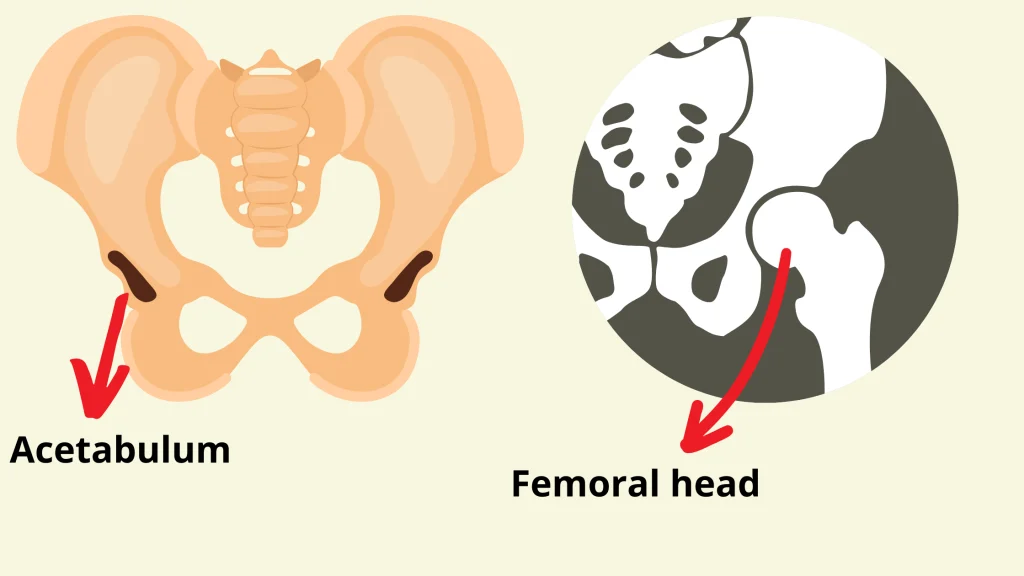
The hip arthroplasty consists of two components, the femoral part, which is inserted into the bone marrow, and the cotyloid part, which is fixed to the pelvis.
It is recommended in patients between 60 and 75 years.
A fixed dome, defined as the prosthetic head, is applied to the femur and inserted into the fixed component in the pelvis.
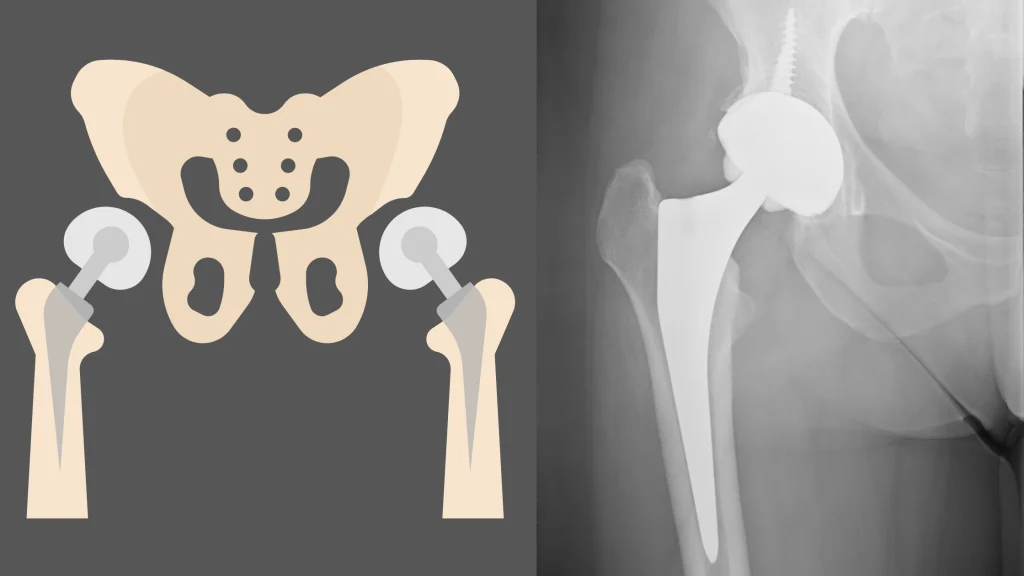
On the contrary, in the endoprosthesis, only the femoral portion is replaced, without performing any particular surgical treatments on the pelvis joint.
If the cartilage is in good condition, there is no need to do any hip surgery.
A metal head (dome) is applied to the femur, which articulates with the patient's cup.
It is recommended in patients over 75 years, because it is simpler, faster and less risky for the elderly patients.
Furthermore, with a total hip prosthesis, post-operative precautions are few.
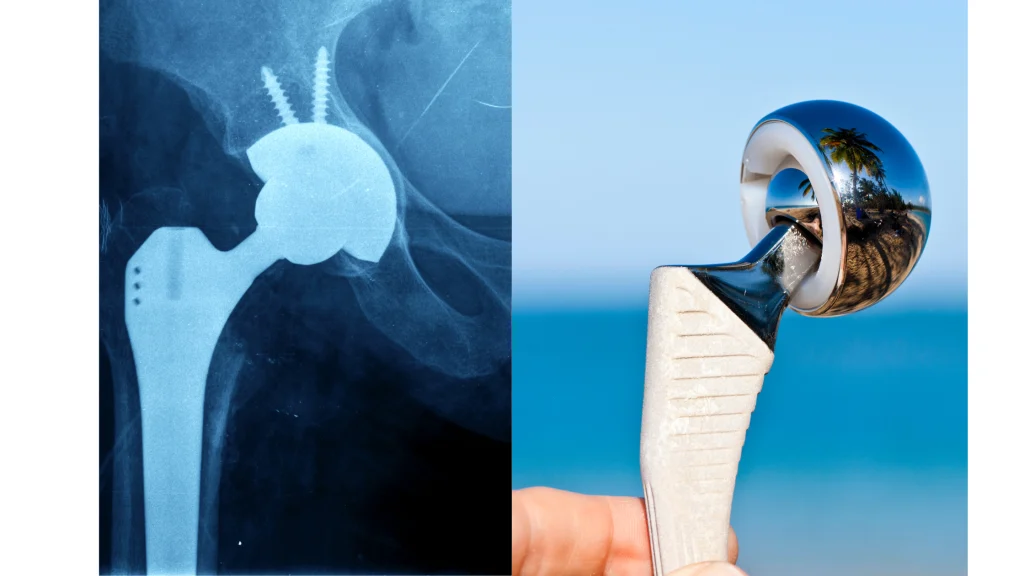
On the other hand, the resurfacing prosthesis only provides the resurfacing of the acetabular component and the femoral head, thus replacing the cartilage worn by arthrosis.
The advantage of this type of prosthesis is that it does not upset the anatomical profile of the joint and, consequently, avoids length differences of the limbs.
It also reduces the risk of implant dislocation (luxation).
Cemented prosthesis allows you to quickly recover the limb strength after the operation, giving you the possibility to walk almost immediately, and avoiding the complications due to immobilization.
The load on the limb is to be considered complete already after the operation.
Conversely, if the prosthesis is not cemented, it is recommended to limit the load on the operated limb, from the first postoperative week, up to 3 months, the right time for an effective rehabilitation.
The difficulty during the walk in the first postoperative period is caused by the inhibition that the body adopts to protect all the affected structures.
So all the muscles, joints, the nerves, etc., are working a bit slower than normal.
It is recommended in patients over 60 years old.
However it is contraindicated, for patients who are severely overweight or are physically very active.